define positive cuurent potassium chanel | Inwardly Rectifying Potassium Channels: Their Structure, define positive cuurent potassium chanel Potassium channels function to conduct potassium ions down their electrochemical gradient, doing so both rapidly (up to the diffusion rate of K ions in bulk water) and selectively (excluding, most notably, sodium despite the sub-angstrom difference in ionic . See more
This reversible belt associates the iconic LV Initiales buckle in dark ruthenium with our new Monogram Eclipse canvas. Subtly branded, it is a perfect match for the Maison's leather goods and shoes. 90 x 4 cm
0 · Voltage
1 · Potassium channel
2 · Potassium Channels, Structure and Function
3 · Potassium Channels in the Heart
4 · Potassium Channel
5 · Pharmacology of cardiac potassium cha
6 · K+ Channels: Function‐Structural Overview
7 · Inwardly Rectifying Potassium Channels: Their Structure,
8 · Inward
Learn More About Our Programs and Resources. Our programs in Southern Nevada include a homeless shelter, food pantry, immigration services, and more. We have a number of resources to support you. Food Services.
Potassium channels are ion channels that regulate potassium ion flow across cell membranes. They are classified into four major classes based on their activation mechanism, function and blockers. Learn more about the calcium-activated, inwardly rectifying, voltage-gated and tandem pore domain potassium . See morePotassium channels are the most widely distributed type of ion channel found in virtually all organisms. They form potassium-selective pores that span cell membranes. Potassium channels are found in most See moreThere are four major classes of potassium channels:• Calcium-activated potassium channel - open in response to the presence of calcium ions or other signalling molecules.• Inwardly rectifying potassium channel - passes current . See moreThe flux of ions through the potassium channel pore is regulated by two related processes, termed gating and inactivation. Gating is the opening or closing of the channel in response . See more
Some types of potassium channels are activated by muscarinic receptors and these are called muscarinic potassium channels (IKACh). These channels are a heterotetramer . See morePotassium channels function to conduct potassium ions down their electrochemical gradient, doing so both rapidly (up to the diffusion rate of K ions in bulk water) and selectively (excluding, most notably, sodium despite the sub-angstrom difference in ionic . See morePotassium channels have a tetrameric structure in which four identical protein subunits associate to form a fourfold symmetric See moreBlockersPotassium channel blockers inhibit the flow of potassium ions through the channel. They either . See more
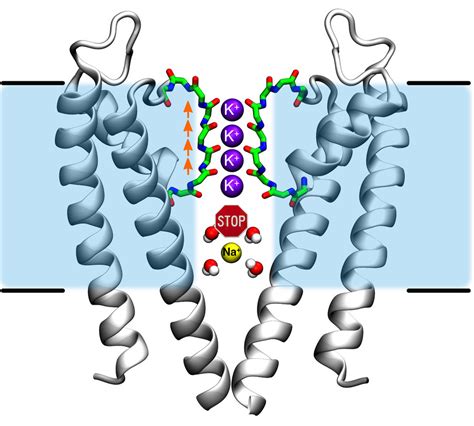
It exhibits a large inward current at the E m more negative than E K and a relatively large outward current at the E m slightly more positive than E K. This feature is essential to .Inward-rectifier potassium channels (Kir, IRK) are a specific lipid-gated subset of potassium channels. To date, seven subfamilies have been identified in various mammalian cell types, plants, and bacteria. They are activated by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2). The malfunction of the channels has been implicated in several diseases. IRK channels possess a pore domai.A major family of potassium channels is the voltage-gated potassium channels (Kv), which detect changes in transmembrane voltage and couple this detection to channel opening and closing. Learn about the structure and function of voltage-gated ion channels, which are transmembrane proteins that change permeability in response to membrane voltage. Find out how activation gates and inactivation .
Learn about the molecular architecture and selectivity of potassium channels, integral membrane proteins that allow K + ions to flow across cell membranes. Explore the structural and . Learn about the definition, structure, function and diversity of potassium channels, a type of membrane protein that regulates ion transport and signaling. Explore chapters and .
Four different subfamilies of potassium channels are present in the heart: small conductance, calcium-activated potassium channels (SK or K Ca 2), inwardly rectifying .The human genome encodes 40 voltage-gated K + channels (K V), which are involved in diverse physiological processes ranging from repolarization of neuronal and cardiac action potentials,. Potassium channels are particularly important in determining the shape and duration of the action potential, controlling the membrane potential, modulating hormone secretion, .Potassium channels are ion channels that regulate potassium ion flow across cell membranes. They are classified into four major classes based on their activation mechanism, function and blockers. Learn more about the calcium-activated, inwardly rectifying, voltage-gated and tandem pore domain potassium channels.
It exhibits a large inward current at the E m more negative than E K and a relatively large outward current at the E m slightly more positive than E K. This feature is essential to stabilize the E res of cardiac myocytes near E K .Learn about the structure, function, and mechanism of inward-rectifier potassium channels (Kir), a subset of potassium channels that transport K + with greater inward than outward tendency. Find out how they are activated by PIP 2, regulate membrane potential, and are involved in .A major family of potassium channels is the voltage-gated potassium channels (Kv), which detect changes in transmembrane voltage and couple this detection to channel opening and closing.
Learn about the structure and function of voltage-gated ion channels, which are transmembrane proteins that change permeability in response to membrane voltage. Find out how activation gates and inactivation gates regulate the flow of sodium, potassium, calcium and chloride ions in neurons.Learn about the molecular architecture and selectivity of potassium channels, integral membrane proteins that allow K + ions to flow across cell membranes. Explore the structural and functional diversity of K + channels from prokaryotes and eukaryotes, and their roles in .Learn about the definition, structure, function and diversity of potassium channels, a type of membrane protein that regulates ion transport and signaling. Explore chapters and articles from various fields of biochemistry, genetics and molecular biology.
Four different subfamilies of potassium channels are present in the heart: small conductance, calcium-activated potassium channels (SK or K Ca 2), inwardly rectifying potassium channels (K ir), two-pore-domain potassium channels (K 2P), and voltage-gated potassium channels (K V).The human genome encodes 40 voltage-gated K + channels (K V), which are involved in diverse physiological processes ranging from repolarization of neuronal and cardiac action potentials,. Potassium channels are particularly important in determining the shape and duration of the action potential, controlling the membrane potential, modulating hormone secretion, epithelial function and, in the case of those K + channels activated by .Potassium channels are ion channels that regulate potassium ion flow across cell membranes. They are classified into four major classes based on their activation mechanism, function and blockers. Learn more about the calcium-activated, inwardly rectifying, voltage-gated and tandem pore domain potassium channels.
louis vuitton sonnenbrille damen 2021
It exhibits a large inward current at the E m more negative than E K and a relatively large outward current at the E m slightly more positive than E K. This feature is essential to stabilize the E res of cardiac myocytes near E K .Learn about the structure, function, and mechanism of inward-rectifier potassium channels (Kir), a subset of potassium channels that transport K + with greater inward than outward tendency. Find out how they are activated by PIP 2, regulate membrane potential, and are involved in .A major family of potassium channels is the voltage-gated potassium channels (Kv), which detect changes in transmembrane voltage and couple this detection to channel opening and closing.
Learn about the structure and function of voltage-gated ion channels, which are transmembrane proteins that change permeability in response to membrane voltage. Find out how activation gates and inactivation gates regulate the flow of sodium, potassium, calcium and chloride ions in neurons.Learn about the molecular architecture and selectivity of potassium channels, integral membrane proteins that allow K + ions to flow across cell membranes. Explore the structural and functional diversity of K + channels from prokaryotes and eukaryotes, and their roles in .
Learn about the definition, structure, function and diversity of potassium channels, a type of membrane protein that regulates ion transport and signaling. Explore chapters and articles from various fields of biochemistry, genetics and molecular biology. Four different subfamilies of potassium channels are present in the heart: small conductance, calcium-activated potassium channels (SK or K Ca 2), inwardly rectifying potassium channels (K ir), two-pore-domain potassium channels (K 2P), and voltage-gated potassium channels (K V).The human genome encodes 40 voltage-gated K + channels (K V), which are involved in diverse physiological processes ranging from repolarization of neuronal and cardiac action potentials,.
Voltage
Potassium channel
Potassium Channels, Structure and Function
370,00€. Descubre nuestra colección de monederos y carteras pequeñas de mujer - LOUIS VUITTON Página Oficial España.
define positive cuurent potassium chanel|Inwardly Rectifying Potassium Channels: Their Structure,